Summary
In this article we get insights from Dr Mithileysh Sathiyanarayanan the founder and CEO of MIT Square, a product development company. In this article he gives us pointers on what he considers to be the most important practices to implement in an early stage commercialisation venture. The insights are broken down into various categories ranging from market research and competitive analysis to risk assessment and scalability to networking and team-building. We hope this article will give young entrepreneurs some useful tips on what they can do to take their fledgling startup to the next level.
Contributed by Dr Mithileysh Sathiyanarayanan the founder and CEO of MIT Square
Early-stage commercialisation is one of the most critical phases of a business journey, where the entrepreneurs and other team members work really hard in bringing a new product or service to market successfully.
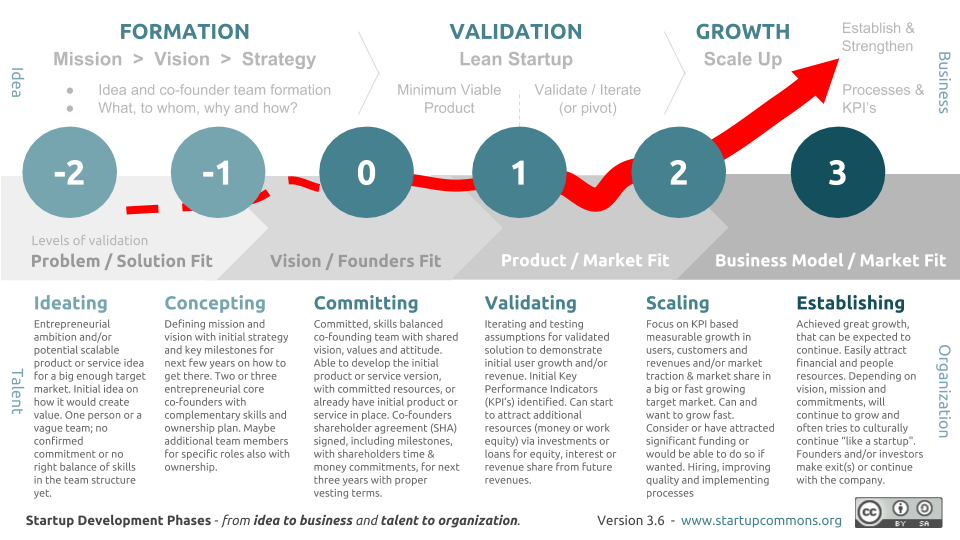
Here are some of the best practices to consider when navigating through this phase. This might help young scientists, professors, researchers or students who are planning to step into the entrepreneurial journey.
- Market Research and Competitive Analysis: Thoroughly research your target market to understand customer needs, preferences, and pain points. Define a clear and compelling value proposition that addresses a specific customer problem or need. Highlight the unique features and benefits of your product or service. Articulate why your offering is superior to alternatives in the market. Continuously monitor the competitive landscape to identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Adjust your strategy accordingly to stay ahead of competitors.
- Business Plan/Model: Develop a comprehensive business plan that outlines your value proposition, revenue model, pricing strategy, and sales and marketing approach. Include financial projections and budgets to plan for growth and sustainability. Develop a clear and sustainable business model that outlines how you will generate revenue. Explore pricing strategies. Establish a sales strategy that outlines how you will reach and engage customers.
- Intellectual Property Rights (IPR) and other Legal Matters: Protect your intellectual property, such as patents, trademarks, or copyrights, to secure a competitive advantage and prevent infringement. Understand and comply with relevant industry regulations and standards. Seek legal counsel to navigate complex regulatory requirements. Embrace sustainable and responsible business practices to enhance your brand reputation.
- Prototype and MVP: Build a minimum viable product (MVP) or prototype to test your concept with real users and gather feedback. Use iterative development to refine your product based on user input.
- Funding Strategy: Evaluate various funding options, such as bootstrapping, angel investors, venture capital, or crowdfunding. Create a compelling pitch and business case for potential investors.
- Marketing and Customer Acquisition : Develop a strong brand identity and marketing strategy to create awareness and generate demand for your product. Utilise digital marketing, content marketing, social media, and other channels as appropriate. Focus on customer acquisition strategies while also prioritising customer retention efforts. Define key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics to measure the success of your commercialisation efforts. Regularly analyse data to make informed decisions and adjustments.
- Continuous Learning and Feedback Loop: Establish a feedback loop with customers, partners, and stakeholders to gather insights and make improvements. Be responsive to user feedback and adapt quickly to changing market dynamics. Stay open to feedback from customers, partners, and advisors. Be willing to pivot and make changes to your product, marketing strategy, or business model based on market feedback.
- Risk Management, Scalability and Flexibility: Identify and mitigate potential risks associated with product development, market volatility, and other factors. Develop contingency plans to address unforeseen challenges. Plan for scalability from the outset to accommodate growth. Ensure that your infrastructure, processes, and resources can scale efficiently.
- Networking and Partnerships: Build relationships with industry influencers, mentors, and potential partners. Leverage networking events, conferences, and industry associations to connect with key players in your field. Assemble a skilled and motivated team with diverse expertise to execute your commercialisation plan. Provide ongoing training and development opportunities.
Early-stage commercialisation is a dynamic process, this phase can be complex and challenging, but following these best practices can increase the chances of building a sustainable and successful business. Adapt various strategies as needed and remain agile to respond to market changes and evolving customer needs. Be prepared to iterate and refine your strategies as you learn from the market and customer feedback. Building a solid foundation in the early stages is essential for long-term success.






